Why Tokenized Reality Is Becoming Crypto’s Most Important Primitive in 2025
For most of its existence, crypto has operated inside a closed financial loop. Tokens were backed by other tokens, yields were generated by leverage rather than productivity, and value creation often depended more on narrative momentum than economic output. That system worked during speculative expansions, but it consistently collapsed under stress.
In 2025, Real World Assets (RWAs) are breaking that loop by anchoring blockchain finance to assets that generate cash flow outside the crypto ecosystem. This is not a cosmetic evolution. It is a structural shift in how capital, risk, and trust are handled on-chain. RWAs are transforming blockchains from speculative networks into settlement layers for real economic activity.
What RWAs Really Represent
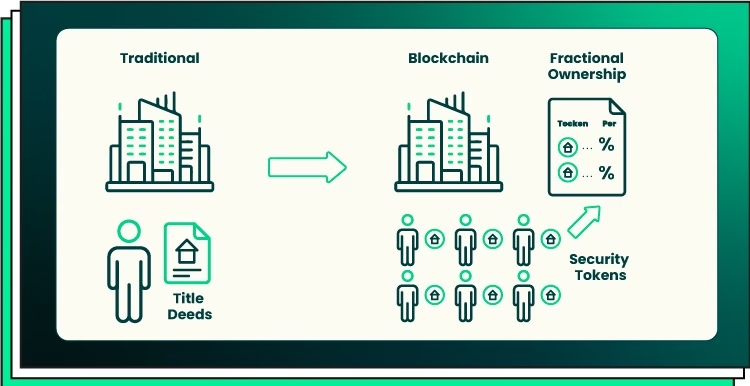
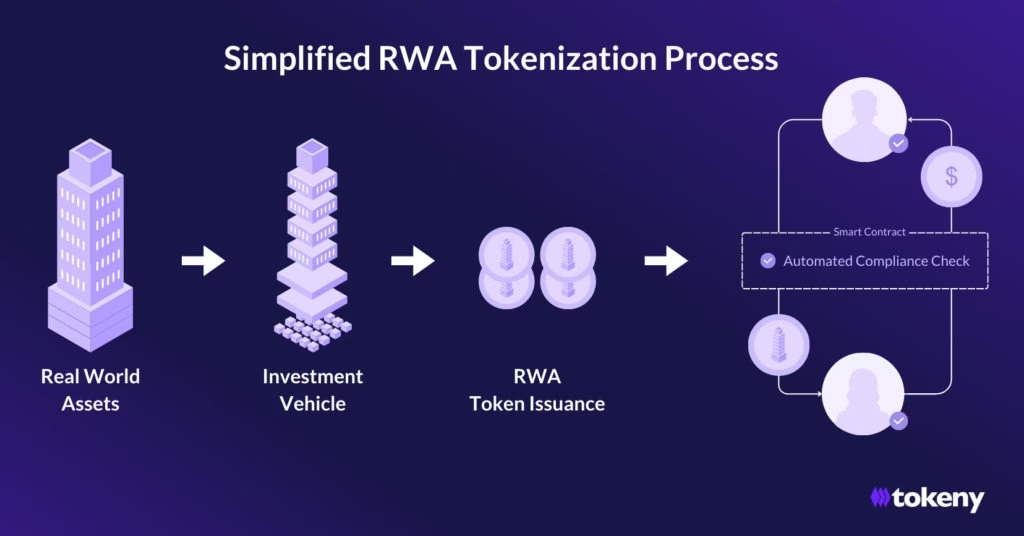
At a technical level, RWAs are blockchain tokens that represent legally enforceable claims on off-chain assets. But reducing RWAs to “tokenization” misses the deeper point. What is being tokenized is not just ownership, it is financial credibility.
An RWA token does three things simultaneously. It digitizes ownership, embeds compliance into transfer logic, and enables programmable interaction with decentralized protocols. When done correctly, it allows an asset governed by courts, contracts, and regulation to interact seamlessly with smart contracts, liquidity pools, and DAOs.
This is why RWAs matter far more than NFTs or memecoins ever did. They introduce productive capital into crypto,assets that pay rent, interest, or fees regardless of market sentiment. In macro terms, RWAs convert blockchain from a speculative market into a capital coordination system.
Why RWAs Are Scaling Now, And Why They Failed Before)
RWAs were attempted many times between 2018 and 2022, and most failed. The reason was not technology, it was alignment. Crypto moved faster than regulators, institutions, and legal systems could tolerate. In 2025, that mismatch has narrowed.
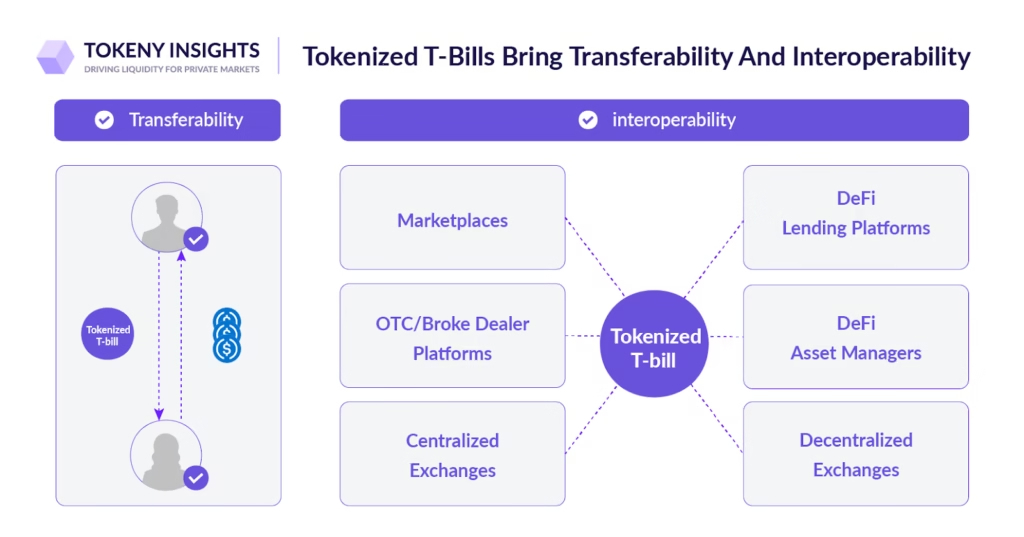
Institutional adoption is the first inflection point. Asset managers, banks, and funds no longer view blockchain as a threat but as financial infrastructure. Tokenized treasuries, money market funds, and credit instruments now offer operational advantages that TradFi systems cannot match: real-time settlement, instant collateral mobility, and transparent balance verification. These advantages are not ideological, they are economic.
The second inflection point is regulatory maturity. Instead of banning or loosely tolerating tokenized securities, jurisdictions like Singapore, Switzerland, the UAE, and the UK now provide explicit legal frameworks for digital asset issuance. Permissioned token standards, on-chain identity verification, and jurisdiction-specific wrappers allow RWAs to exist legally without sacrificing composability.
The third catalyst is DeFi’s survival instinct. After the collapse of inflation-driven yield models, DeFi needed income sources that did not depend on perpetual token issuance. RWAs provided exactly that yield derived from real interest payments, rent, or receivables. In 2025, RWAs are not optional. They are foundational.
Government Debt: The Backbone of On-Chain Yield
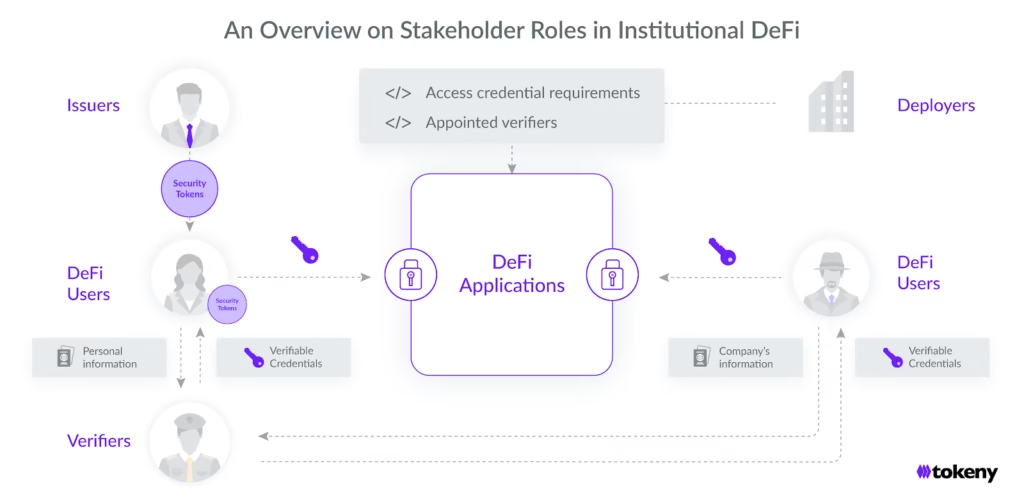
Tokenized government debt is the single most important RWA category today. Short-term U.S. Treasury bills dominate because they combine three properties crypto desperately needs: trust, liquidity, and predictable yield.
When DAOs or protocols hold tokenized T-bills, they gain access to sovereign-grade yield without relying on banks or custodians in the traditional sense. Funds settle instantly. Assets remain visible on-chain. Risk exposure is transparent rather than abstracted behind balance sheets.
This effectively creates a crypto-native money market, where idle capital earns yield while remaining deployable inside DeFi. For the first time, blockchain finance has access to the same baseline yield instruments that underpin traditional capital markets.
Real Estate RWAs: From Speculation to Cash Flow
Tokenized real estate was once marketed as “own a house for $10.” In 2025, that framing has matured. The focus has shifted away from novelty and toward income stability.
Modern real estate RWAs emphasize rental yield, jurisdictional clarity, and predictable distribution mechanisms. Investors are no longer betting on price appreciation alone; they are participating in cash-flow-generating assets without geographic or operational burden.
This matters because real estate has always been one of the most reliable wealth-building tools globally. RWAs are not reinventing property,,they are removing friction from access, ownership, and liquidity.
Trade Finance: The Most Underrated RWA Use Case
Trade finance rarely trends on crypto Twitter, but economically it is enormous. Small and mid-sized businesses worldwide suffer from delayed payments and restricted credit access. RWAs are changing that by allowing receivables and invoices to be tokenized and financed on-chain.
When a logistics firm tokenizes an invoice and borrows stablecoins against it, DeFi becomes a working capital engine rather than a speculative casino. Liquidity moves directly from crypto holders to productive enterprises, bypassing slow and exclusionary banking systems.
This is one of the clearest examples of crypto delivering real-world utility at scale.
Carbon Credits and Environmental Assets
Tokenized carbon credits address one of ESG finance’s biggest problems: trust. Traditional carbon markets suffer from opacity, double counting, and unverifiable claims. Blockchain fixes this by making issuance, transfer, and retirement transparent.
RWAs allow environmental impact to become auditable infrastructure, not marketing language. As regulation tightens around ESG disclosures, on-chain carbon assets are becoming operational tools rather than symbolic gestures.
How RWAs Are Rewriting DeFi Architecture
RWAs are forcing DeFi protocols to evolve. Lending platforms now resemble credit desks. Stablecoins resemble regulated money funds. DAOs operate more like treasury managers than speculative collectives.
This convergence is not accidental. It reflects a deeper truth: finance converges toward efficiency. RWAs make DeFi more boring and far more durable.
Structural Risks That Still Matter
RWAs reduce volatility risk, but they introduce legal and operational risk. Custodians hold underlying assets. Courts enforce claims. Oracles bridge off-chain reality to on-chain logic.
The difference in 2025 is not that these risks disappeared, it’s that they are now explicit, priced, and engineered around. That alone marks a massive step forward from earlier crypto cycles.
Where RWAs Are Headed Next

RWAs are evolving from isolated products into financial primitives. Expect tokenized yield curves, AI-driven credit scoring, cross-chain RWA liquidity, and retail access through invisible blockchain layers.
The long-term outcome is clear: programmable finance grounded in real economic output.
RWAs Are Crypto’s Maturity Moment
Crypto does not replace traditional finance by rejecting it. It replaces it by absorbing its strongest components and removing inefficiencies.
RWAs are that absorption layer.They transform blockchains from speculative arenas into capital markets, from narrative engines into settlement networks, and from volatile ecosystems into durable financial infrastructure.
In 2025, RWAs are not a trend.
They are crypto growing up.
Related Articles
- Ethereum vs Solana: which smart contract platform really wins on speed, cost, and ecosystem strength?
- Beginner’s guide: how to earn real passive income from DeFi lending without blowing up your capital
- How to build a balanced crypto portfolio that works in both brutal bear phases and euphoric bull runs (2025 blueprint)
- Ultimate 2025 guide: how to protect your seed phrase from theft, fire, and family members
- Crypto taxes made simple: how to report, calculate, and file your crypto gains without costly mistakes





