The internet is quietly undergoing its most important transformation since the rise of social media. After decades of centralized platforms controlling data, money, and digital identity, a new model is emerging Web3. It is not a single product, company, or app. It is a structural shift in how the internet works and who benefits from it.
Web3 aims to correct the power imbalance created during the Web2 era, where users generate value while platforms capture it. Instead of platforms owning data and monetizing attention, Web3 introduces ownership, transparency, and programmable trust at the protocol level.
Understanding Web3 is no longer optional for developers or investors, it matters to anyone who uses the internet.
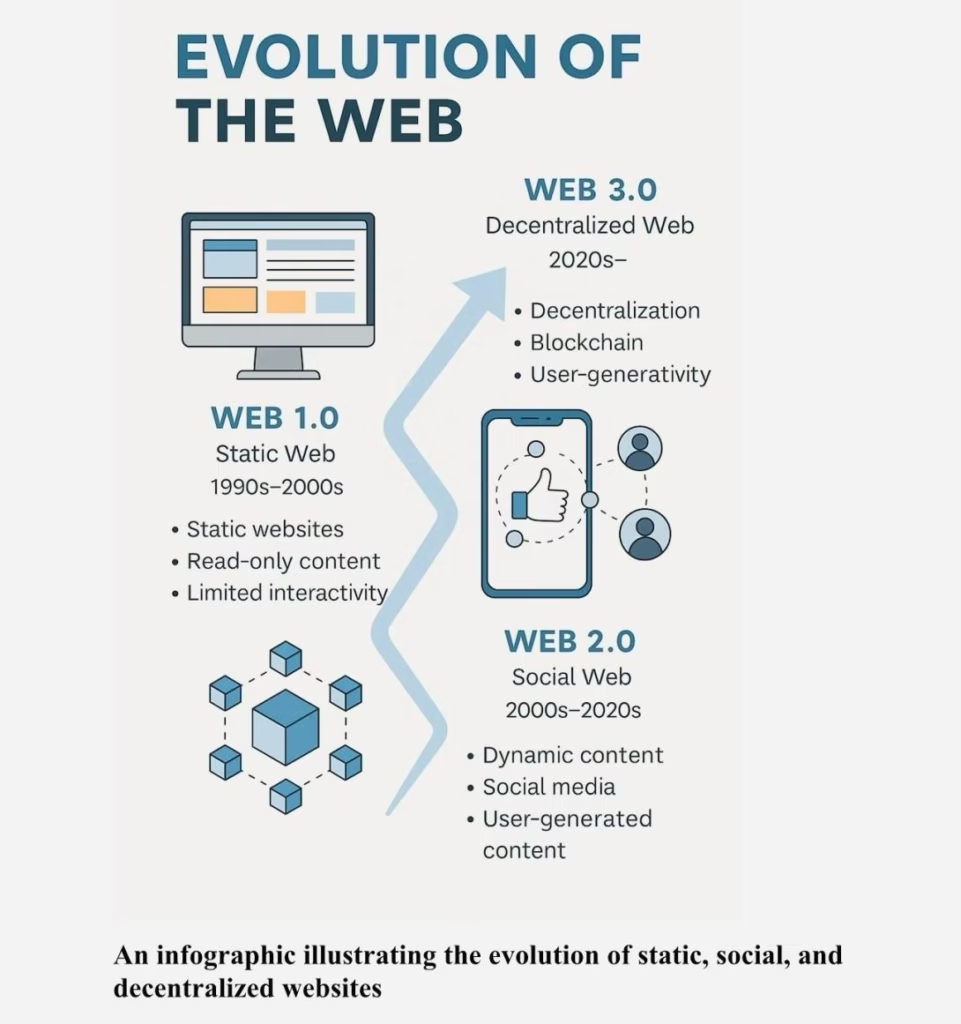
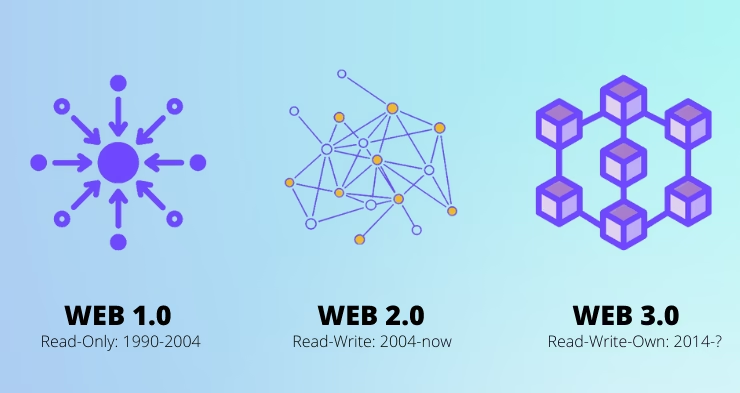
Defining Web3: The Decentralized Web Explained Clearly
Web3 refers to the third generation of internet architecture, built on blockchain networks, cryptography, and decentralized protocols.
To understand it properly, it helps to see the evolution:
| Internet Era | Core Capability | Who Owns Data |
| Web1 | Read | Websites |
| Web2 | Read + Write | Platforms |
| Web3 | Read + Write + Own | Users |
In Web3, users interact through wallets, not accounts. Assets live on blockchains, not company servers. Identity is portable, programmable, and permissionless.
At its core, Web3 enables users to:
- Own digital assets directly
- Participate in governance
- Earn from contributions
- Transact without intermediaries
- Verify trust through code instead of institutions
Why Web3 Matters: More Than Just Technology
Web3 is not important because it uses blockchains. It matters because it restructures incentives across the internet.
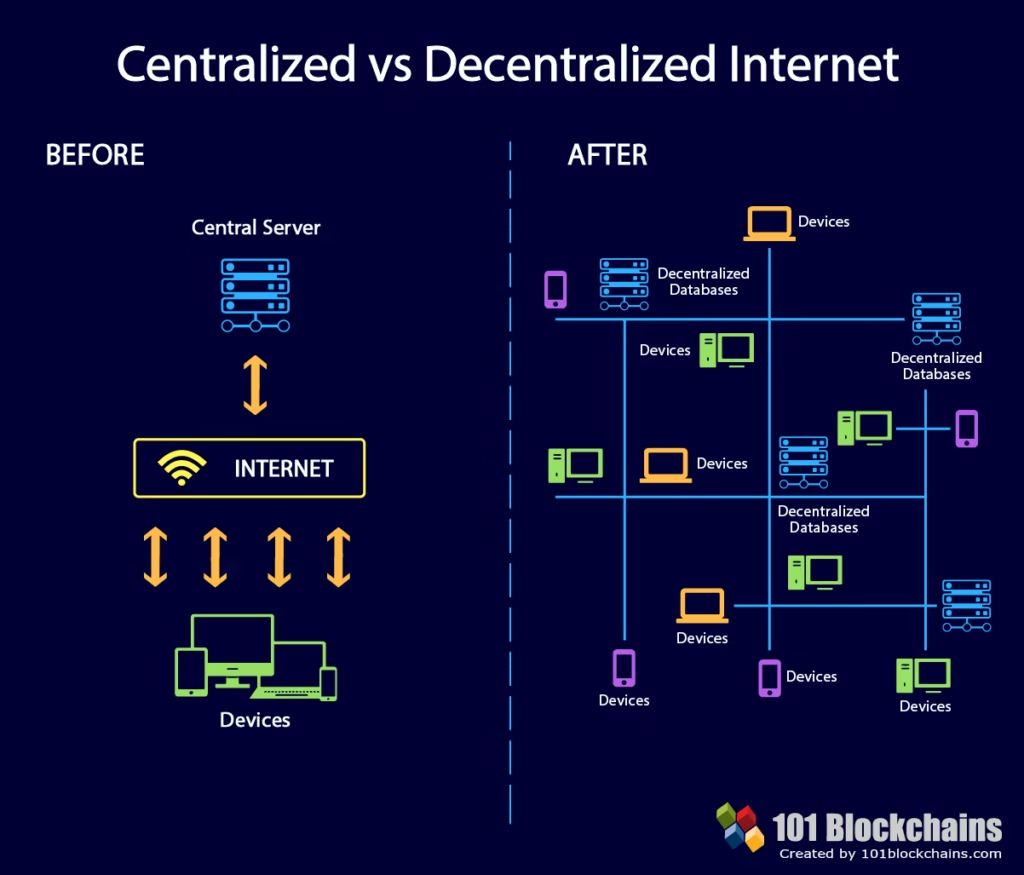
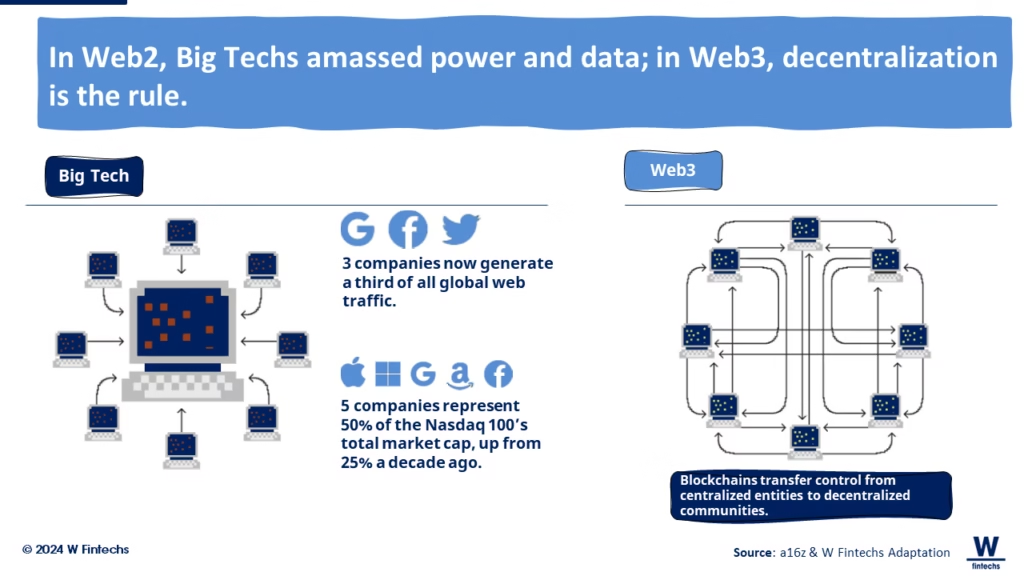
1. Ownership Replaces Rent-Seeking
In Web2, platforms extract value continuously through ads, fees, or data harvesting. In Web3, value accrues to users, creators, and contributors through tokens and ownership.
Your NFT, tokens, or identity are not hosted by a platform. They exist independently of it.
2. Trust Becomes Programmable
Smart contracts replace intermediaries with deterministic code. This removes:
- Banks from settlements
- Platforms from payments
- Brokers from coordination
The result is faster execution, lower costs, and verifiable transparency.
3. Economic Participation Is Built-In
Web3 applications embed incentives directly into their design:
- Liquidity providers earn yield
- DAO contributors earn governance power
- Creators earn royalties automatically
This shifts the internet from attention extraction to value participation.
4. Censorship Resistance and Global Access
Decentralized networks are harder to shut down or control. This matters for users in regions with financial restrictions, unstable institutions, or censorship.
The Technology Stack Powering Web3
Web3 is built on a layered technical foundation. Understanding this stack helps separate substance from hype.

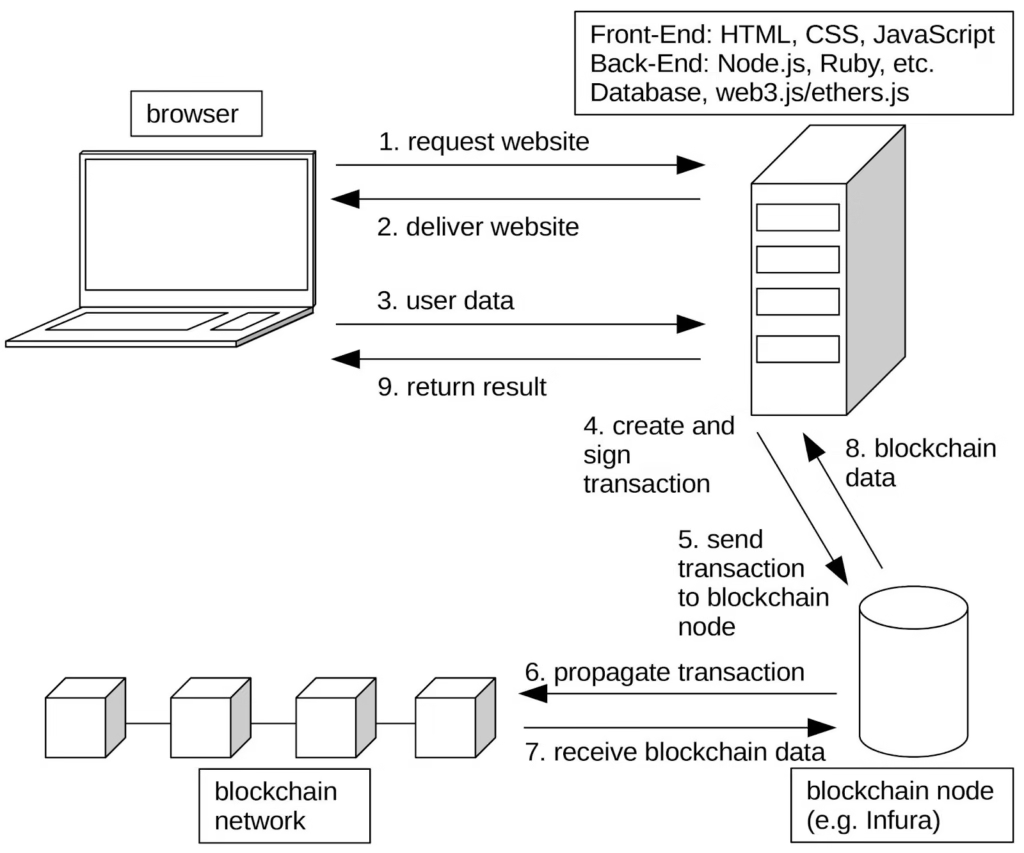
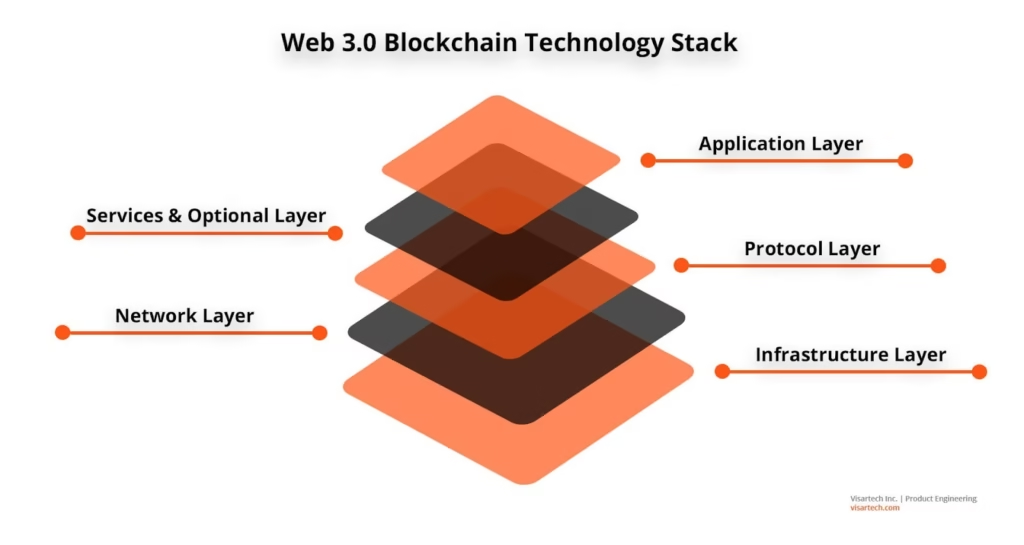
| Layer | Purpose |
| Blockchains | Immutable settlement & consensus |
| Smart Contracts | On-chain logic and automation |
| Tokens | Value transfer, governance, incentives |
| Decentralized Storage | Peer-to-peer data hosting |
| Wallets | Identity and access layer |
| dApps | User-facing applications |
This modular structure allows Web3 to evolve rapidly without central control.
Web3 in Action: Real Use Cases Today
Web3 is already operational across multiple industries.
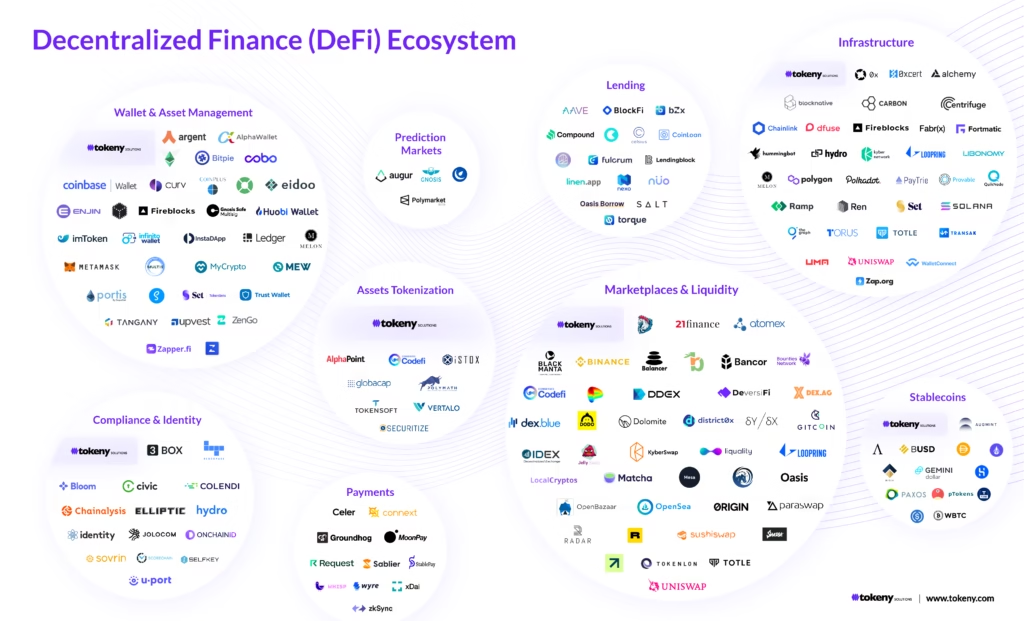
Key Use Cases
| Sector | What Web3 Enables |
| Finance | DeFi lending, trading, stablecoins |
| Art & Media | NFTs with enforced royalties |
| Gaming | Player-owned economies |
| Governance | DAOs with transparent voting |
| Identity | Wallet-based digital identity |
| Social | Creator-owned audiences |
This is not speculative infrastructure,it is live, used, and growing.
How You Can Join Web3?
Joining Web3 does not require technical expertise, but it does require intentional learning.

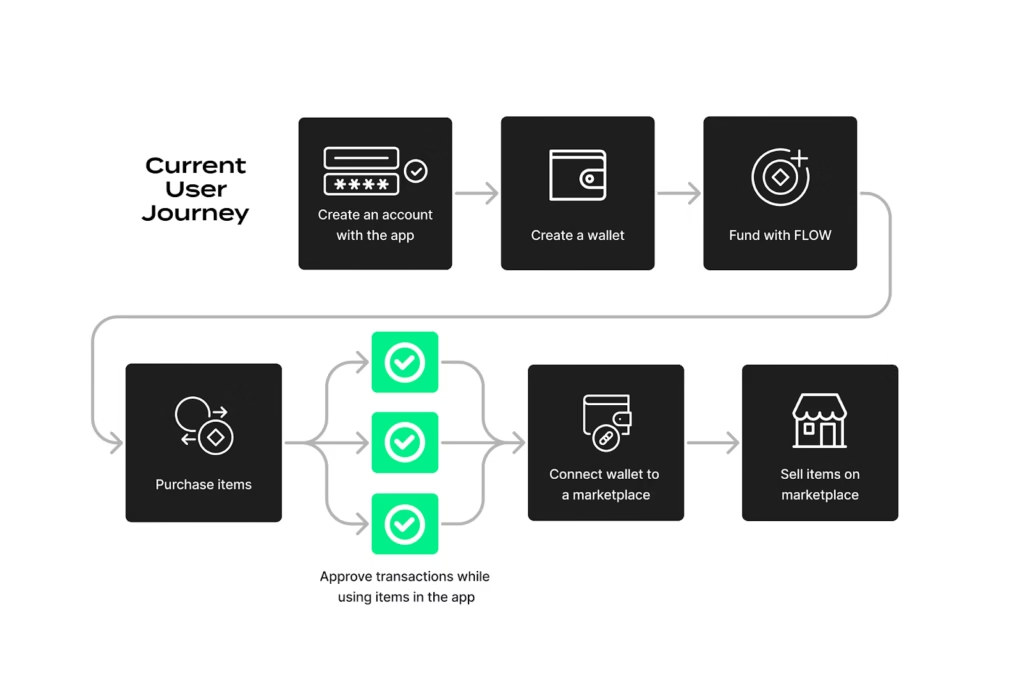
1. Set Up a Non-Custodial Wallet
Install a wallet such as MetaMask, Phantom, or Keplr. This becomes your digital identity. Your seed phrase is your ownership, protect it offline.
2. Acquire Small Amounts of Crypto
Use a regulated exchange to buy ETH, SOL, or another base asset. Start small. Treat early transactions as education.
3. Interact With dApps
Try basic actions:
- Swap tokens
- Mint an NFT
- Stake assets
- Vote in a DAO
Experience builds understanding.
4. Join Communities
Web3 is social by design. DAOs and open communities are where learning, contribution, and opportunity intersect.
5. Keep Learning
The ecosystem evolves rapidly. Continuous learning is not optional, it’s the cost of participation.
Challenges Web3 Still Faces:
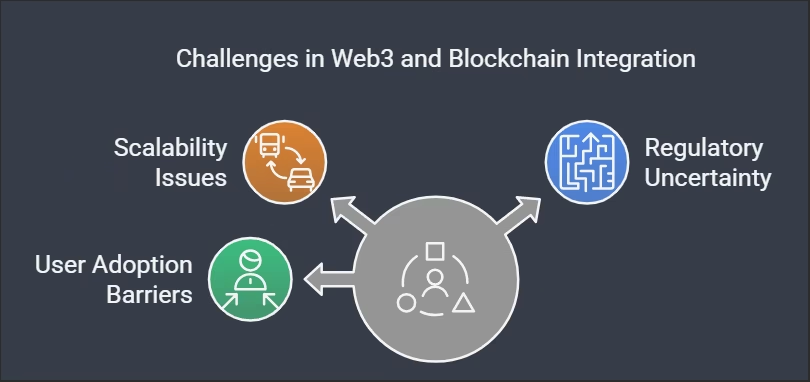
| Challenge | Reality |
| Scalability | Layer 2s are actively solving this |
| Regulation | Frameworks are forming globally |
| UX Complexity | Improving rapidly with abstraction |
| Security Risks | Education + better tooling reduce exposure |
These are growing pains, not dead ends.
Final Perspective: Why Web3 Is Inevitable
Web3 is not replacing the internet, it is rebalancing it.
It shifts:
- From platforms to protocols
- From renters to owners
- From opaque systems to verifiable ones
You don’t need to become a developer or investor to benefit. Participation itself, learning, owning, contributing is the real entry point.
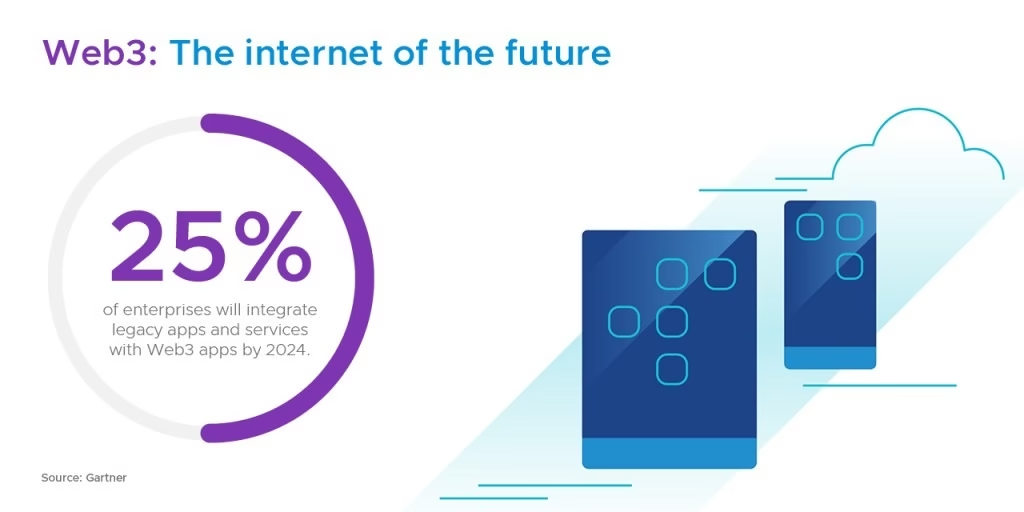
Web3 will not arrive overnight. It will emerge gradually, unevenly, and sometimes painfully. But once ownership becomes native to the internet, there is no going back.
Related Articles
- Crypto taxes made simple: how to report, calculate, and file your crypto gains without costly mistakes
- How to safely buy Bitcoin in 2025: a complete beginner’s roadmap with pro-level
- Beginner’s guide: how to earn real passive income from DeFi lending without blowing up your capital
- 10 common crypto scams and exactly how to avoid losing your money to them
- Why you should never leave your crypto on an exchange and the safer storage options professionals actually use
- Ethereum vs Solana: which smart contract platform really wins on speed, cost, and ecosystem strength?





